A new report by the World Bank has revealed that Ghana was the second top recipient of remittances in sub Saharan Africa in 2023. In 2022, Ghana recorded $4.7 billion in remittances occupying the second position in that year.
This was captured in the 2023 Migration and Development report released by bank on June 26, 2024.
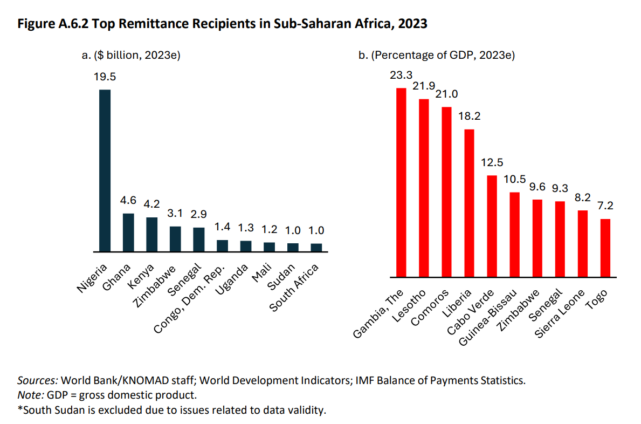
According to the report, the largest recipients of remittances in the period under review in US dollar terms were Nigeria, followed by Ghana, Kenya, and Zimbabwe.
Nigeria received $19.5 billion, Ghana $4.6 billion, Kenya $4.2 billion and Zimbabwe $2.1 billion.
The report pointed out that remittances have become the most important foreign exchange earner in most countries in sub Saharan Africa.
“For example, for Kenya remittances are larger than the country’s key exports, including tourism, tea, coffee, and horticulture. Countries more dependent on receipts as a proportion of GDP include the Gambia, Lesotho, Comoros, Liberia, and Cabo Verde with remittances contributing more than a fifth of GDP in the first three countries”, it said.
The World Bank explained thatremittance flows to Sub-Saharan Africa were nearly 1.5 times the size of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows in 2023, and relatively more stable.
Over all, the report said that the regional growth in remittances in 2023 was largely driven by strong remittance growth in Uganda (15 percent to $1.4 billion), Rwanda (9.3 percent to $0.5 billion), Kenya (2.6 percent to $4.2 billion), and Tanzania (4 percent to $0.7 billion). Remittances to Nigeria, accounting for around 35 percent of total remittance inflows to the region, decreased by 2.9 percent to $19.5 billion.
Remittance costs
The report revealed that sub-Saharan Africa remained the region with the highest remittance costs. Senders had to pay an average of 7.9 percent to send $200 to African countries during 2023Q4, compared with 7.4 percent in 2022Q4.
Costs vary substantially across the region, ranging from 2.1–4.0 percent in the lowest-cost corridors to 18–36 percent in the highest.
Intraregional remittances costs are still very high. For example, sending $200 in remittances from Tanzania to neighboring Kenya, Uganda, and Rwanda cost a migrant more than 33 percent in 2023Q4.







